What are the heat treatment process terms?
The terminology of heat treatment process is to make everyone have an accurate and scientific terminology in the formulation of process standards or technical exchanges. Its content is extensive. China has GB/T7232 "metal heat treatment process terminology" standard. The general category of terms has the following contents:
Overall heat treatment, chemical heat treatment, surface heat treatment, preliminary heat treatment, vacuum heat treatment, high energy beam heat treatment, bright heat treatment, fluidized bed heat treatment, magnetic field heat treatment, protective atmosphere heat treatment, stabilization heat treatment, cleaning heat treatment, repair heat treatment, ion bombardment heat treatment, and the like.
How to mark the heat treatment technical conditions on the drawings?
There are two ways to express the technical conditions for heat treatment on the drawings: one is to use standardized symbols and codes, and the words are used in the blank space of the drawings. For more requirements, separate writing technical requirements, such as hardness requirements: numbers +HRC, the hardness can be marked by the range, for example: 50 ~ 55HRC, can also use the deviation representation: for example 55 ± 2HRC.
Carburizing depth: ≥0.3~0.5mm. The other is that the text is labeled in the figure, see the legend below.
(1) normalizing, annealing, quenching and tempering, quenching and tempering heat treatment
The heat treatment hardness requirements for normalizing, annealing, and quenching are usually expressed in terms of Brinell hardness; the high hardness value of quenching and tempering is usually expressed in Rockwell hardness, and the Brinell hardness can also be expressed in low hardness.
The hardness range (tolerance) must be stated when setting the hardness. It cannot be expressed by a single number. Due to the influence of the chemical composition of the material, the uniformity of the heating furnace, the shape of the workpiece, etc., it is impossible to achieve the hardness value of the same batch or the same workpiece. Hardness value. In practical production, it is often encountered in the technical standards that the hardness requirement of 1HRC is required, which is impossible to achieve. The tolerances for hardness values ​​can be found in Table 4-1:
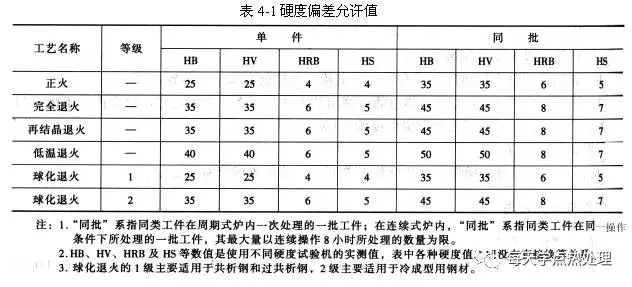

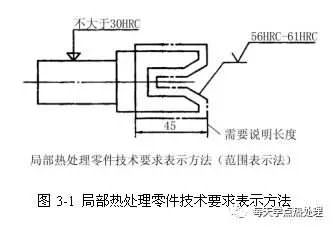
(2) induction surface quenching and tempering treatment
Surface hardness values ​​are expressed in terms of Vickers hardness and generally include surface hardness and quench hardening depth values. a, the surface hardness consists of two parts: the hardness value and the corresponding hardness test force, for example: hardness number + HVx (x indicates the test force used), b, effective hardening depth of quenching, effective hardening depth consists of three parts, hardened layer Code: DS, unit mm, boundary hardness value and required depth. C. Core hardness: The hardness of the core can be determined by using the hardness value of the preliminary heat treatment.
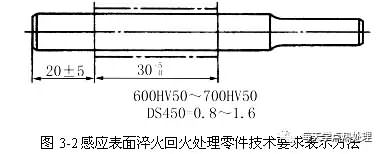
In the drawing, the heat treatment part must be marked. The induction surface of a shaft part is quenched. It starts at 20±5mm from the shaft end and is heat treated in the length of 30mm+5mm. The surface hardness requires 600HV50~700HV50. The effective hardened layer depth DS requirements The 0.8~1.6mm labeling method is shown in Figure 3-2 below:
(3) Carburizing, carbonitriding heat treatment
Technical conditions for carburizing and carbonitriding heat treatment include surface hardness, core hardness, and effective hardened layer depth. a. The surface hardness is similar to the induction heat treatment, using Vickers hardness or Rockwell hardness. b. When there is a requirement for the hardness of the heart, make a mark. c. The effective hardened layer depth is represented by the symbol DC, and the unit uses mm, which is generally divided by 550HV1.
For partially carburized workpieces, they should be marked on the drawing.(4) Nitriding treatment
Technical conditions for nitriding include surface hardness, core hardness, and total nitriding layer depth. a. Surface hardness is marked similar to carburizing, using Vickers hardness. b. When the hardness of the core is required, it shall be marked, generally based on the hardness of the substrate preliminary heat treatment. c. The total nitriding depth is represented by the symbol DN, and the unit uses mm, including the compound layer and the diffusion layer.
What is the principle of heat treatment process preparation?
The heat treatment process is a processing method summarized after production practice, which is scientific, accurate and advanced. The quality of the product depends first and foremost on the correctness and reliability of the process. Economic efficiency is determined by the rationality and advancement of the process. Therefore, the following principles must be followed when preparing the heat treatment process:
(1) Advancement and feasibility of the process: determined according to the specific conditions of the enterprise, including equipment accuracy, personnel quality, and management level. Where these conditions permit, new materials are used and new processes are used to improve or stabilize the heat treatment quality of the part.
(2) Correctness and rationality of the process: The formulation of the heat treatment process must be based on the conditions of use and performance of the parts, scientific analysis, selection of correct and appropriate process plans, process parameters to be tested and verified, and combined The actual conditions of the production equipment of the production unit to avoid blindness.
(3) Economical process: When several processes can meet the requirements of use, the existing heat treatment conditions, such as equipment, quenching medium, fixtures, etc., should be selected to simplify the process, high production efficiency and low energy consumption. The operation is simple and reliable.
(4) Safety of the process: When formulating the heat treatment process, it is necessary to ensure production safety, reduce the labor intensity of workers, and use non-polluting quenching medium as much as possible to control and discharge the polluted gas and wastewater. Improve workers' labor protection. Processes that are nuisance must be eliminated in the process.
(5) Standardization and traceability of the process. This is a key part of modern enterprise management. It adopts national standards or norms, and the whole process of production must be recorded. All production and test data must have files. The product can be traced, the accident can be traced and analyzed, the cause can be found, preventive measures can be proposed, and the process level can be improved.
What are the basis for the preparation of heat treatment process?
Understand the working conditions, service status, part drawings and technical conditions of the part. Understand the entire process route of the part, the cold and hot processing conditions and quality before and after the heat treatment, and the actual production conditions of the workshop now or in the past. Collect relevant materials, heat treatment process parameters, heat treatment technical data of similar products of this enterprise or other enterprises. National and industry standards, heat treatment technical materials and manuals. The shape, size, weight, etc. of the actual workpiece. As well as the production equipment and testing equipment of the company, the quality of workers. The quality of workers is an important factor and cannot be ignored.
BS 4346 Water Supply Fitting With Thread
Pvc Male Plug,Pressure Pvc Male Plug,Pvc Female Thread Tee,Water Supply Upvc Male End Cap
Zhejiang Huangyan Minghua Plastic Pipe Fitting CO.,LTD , https://www.pipefitting-mh.com