Precision Special Steel New Knowledge: What is Special Steel?
What is special steel?
There is no unified definition and concept for special steels. It is generally believed that special steels refer to steels that have special chemical compositions (alloyed), are produced by special processes, have special structures and properties, and can meet special requirements. Compared with ordinary steel, special steel has higher strength and toughness, physical properties, chemical properties, biocompatibility and process performance.
China and Japan, the European Union, the definition of special steel is relatively close, the special steel is divided into high-quality carbon steel, alloy steel, high alloy steel (alloy elements greater than 10%) three categories, including alloy steel and high alloy steel production of special steel 70%. The main steel grades are special carbon structural steel, carbon tool steel, carbon spring steel, alloy spring steel, alloy structural steel, ball bearing steel, alloy tool steel, high alloy tool steel, high speed tool steel, stainless steel, heat-resistant steel , And high-temperature alloys, precision alloys, electric alloys and so on. At present, there are nearly 2,000 special steel grades in the world and about 50,000 specifications. In addition to the wide variety of special steels, the specifications also show different characteristics from ordinary steel. In addition to plates, pipes, wires, belts, rods and profiles, there are composite materials, surface alloying materials, surface treatment materials, precision forging materials, precision castings, and powder metallurgy products.
1. Overview of China's Steel Representation Methods Steel's steel grades are referred to as steel grades, which are the names of each specific steel product and are a common language for people to understand steel. The method for expressing steel numbers in China is represented by the combination of Chinese Pinyin letters, chemical element symbols and Arabic numerals in accordance with the provisions of the national standard “Steel Product Brand Representation Method†(GB221-79). Namely: 1 The chemical elements in the steel number are represented by international chemical symbols, such as Si, Mn, Cr, etc. Mixed rare earth elements are represented by "RE" (or "Xt"). 2 The product name, use, smelting, and pouring methods are generally expressed in the initial alphabet of Chinese pinyin. 3 The content of major chemical elements in steel (%) is expressed in Arabic numerals.
Second, the classification of China's steel representation method 1. The carbon structural steel 1 consists of the Q+ number + quality grade symbol + deoxidation method symbol. Its steel is marked with "Q", which represents the yield point of the steel. The following figures indicate the yield point value in MPa. For example, Q235 indicates carbon structural steel with a yield point (σs) of 235 MPa.
2 If necessary, symbols indicating the quality level and deoxidation method may be marked after the steel number. The quality grade symbols are A, B, C, and D, respectively. Deoxidation method symbol: F for boiling steel; b for semi-static steel: Z for killed steel; TZ for special killed steel, killed steel may not be a symbol, that is, Z and TZ can not mark. For example, Q235-AF indicates Grade A boiling steel.
3 Carbon steels for special purposes, such as bridge steels, shipbuilding steels, etc., basically use the expression of carbon structural steels, but at the end of the steel grade, the letters that indicate the use are added.
2. Two digits at the beginning of a high-quality carbon structural steel 1 steel number indicate the carbon content of the steel, expressed in parts per million of the average carbon content. For example, steel with an average carbon content of 0.45% and a steel number of “45†is not a sequence number. , so can't read 45 steel.
2 High-quality carbon structural steel with high manganese content should be marked with manganese, such as 50Mn. 3 Boiling steel, semi-killed steel and special-purpose high-quality carbon structural steels shall be specially marked at the end of the steel grade. For example, semi-static steel with an average carbon content of 0.1% shall be 10b.
3. Carbon tool steel 1 steel with "T" to avoid mixing with other steels.
The number in 2 steel indicates the carbon content, expressed as a few thousandth of the average carbon content. For example "T8" means that the average carbon content is 0.8%.
3 If the manganese content is higher, “Mn†is marked at the end of the steel number, such as “T8Mnâ€.
4 The phosphorus and sulfur content of the high-quality high-quality carbon tool steel is lower than that of ordinary high-quality carbon tool steel. The letter “A†is added at the end of the steel number to show the difference, such as “T8MnAâ€.
4. Free-cutting steel No. 1 is crowned with "Y" to distinguish it from high-quality carbon structural steel.
The number after the 2 letter “Y†indicates the carbon content, expressed in parts per million of the average carbon content, for example free cutting steel with an average carbon content of 0.3%, whose steel number is “Y30â€.
3 If the manganese content is higher, “Mn†is also marked after the steel number, for example “Y40Mnâ€.
5. Alloy structural steel The two digits at the beginning of a steel number indicate the carbon content of the steel, expressed as a fraction of the average carbon content, such as 40Cr.
2 The major alloying elements in steel, except for individual microalloying elements, are generally expressed in percent. When the average alloy content is less than 1.5%, only the symbol of the element is generally marked in the steel number, but the content is not marked, but in special circumstances, it is easy to cause confusion. After the element symbol, the number “1†may also be marked, for example, the steel number. "12CrMoV" and "12Cr1MoV", the former chromium content of 0.4-0.6%, the latter is 0.9-1.2%, and the remaining components are all the same. When the average content of alloying elements is ≥ 1.5%, ≥ 2.5%, ≥ 3.5%, etc., the content shall be indicated after the element symbol, which may be expressed as 2, 3, 4...etc. For example 18Cr2Ni4WA.
(3) Alloying elements such as vanadium V, titanium Ti, aluminum AL, boron B, and rare earth RE in steel are microalloying elements. Although the content is very low, they should be marked in the steel number. For example, in 20MnVB steel. Vanadium is 0.07-0.12% and boron is 0.001-0.005%.
4 High-quality steel should be added "A" at the end of the steel to distinguish it from ordinary high-grade steel.
5 special purpose alloy structural steel, steel crown (or suffix) represents the symbol of the steel use. For example, special 30CrMnSi steel for rivets, the steel number is ML30CrMnSi.
6. The low-alloy high-strength steel 1 steel is basically the same as the alloy structural steel.
2 For the professional use of low-alloy high-strength steel, should be marked at the end of the steel number. For example, for 16Mn steel, special steel grades for bridges are “16Mnqâ€, special grades for automobile girders are “16MnLâ€, and special steel grades for pressure vessels are “16MnRâ€.
7. Spring steel spring steel can be divided into two types according to the chemical composition of carbon spring steel and alloy spring steel. The steel number indicates the method. The former is basically the same as the high-quality carbon structural steel, and the latter is basically the same as the alloy steel.
8. Rolling bearing steel 1 Steel crown with the letter "G", indicating rolling bearing steel.
2 Carbon content of high carbon chromium bearing steel grades is not marked, chromium content is expressed in parts per thousand such as GCr15. Carburized bearing steel steel representation method is basically the same as alloy structural steel.
9. Alloy tool steels and high-speed tool steels 1 Alloy tool steels with an average carbon content of ≥1.0% do not indicate carbon content; when the average carbon content is <1.0%, they are expressed in parts per thousand. For example, Cr12, CrWMn, 9SiCr, 3Cr2W8V.
2 The expression of alloying elements in steel is basically the same as that of alloy structural steels. However, for alloy steels with lower chromium content, the chromium content is expressed in parts per thousand, and “0†is added before the figure indicating the content, so that it is expressed as a percentage of the general element content. Differentiate. For example Cr06.
3 The steel number of high-speed tool steel is generally not marked with carbon content, only a few percent of the average content of various alloy elements. For example, the steel grade of tungsten high speed steel is expressed as "W18Cr4V". Steel grades with the letter "C" indicate that their carbon content is higher than that of the unbranded "C."
10. Stainless steel and heat-resisting steel 1 The carbon content of steel No. 1 is expressed in parts per thousand. For example, the average carbon content of “2Cr13†steel is 0.2%; if the carbon content in steel is ≤0.03% or ≤0.08%, the steel number is preceded by “00†and "0" respectively, such as 00Cr17Ni14Mo2, 0Cr18Ni9, etc. .
2 The major alloying elements in the steel are expressed in percent, while titanium, niobium, zirconium, nitrogen, etc. are marked according to the above-mentioned method of expressing the alloying steel to the microalloying elements.
11. Welding rod steel is preceded by the letter “H†to distinguish it from other steels. For example, stainless steel wire is "H2Cr13", which can be distinguished from stainless steel "2Cr13".
12. Electrical steel silicon steel 1 steel letters and numbers. The steel head letter DR denotes hot-rolled silicon steel for electrical use, DW denotes cold-rolled non-oriented silicon steel for electrical use, and DQ denotes cold-rolled oriented silicon steel for electrical use.
The number after 2 letters represents 100 times the iron loss value (W/kg).
3 Those with steel “G†at the end of the steel mark indicate testing at high frequency; those without “G†indicate testing at a frequency of 50 cycles. For example, steel number DW470 indicates that the maximum unit weight iron loss value of the cold-rolled non-oriented silicon steel products for electrical appliances at a frequency of 50 Hz is 4.7 W/kg.
13. Electric iron used for electricians 1 Its brand name consists of the letters “DT†and numbers. “DT†indicates pure iron for electricians and numbers indicate the serial numbers of different brands, such as DT3.
2 The letters added after the numbers indicate electromagnetic performance: A - Advanced, E - Special, C - Super, such as DT8A.
The Majority of gardeners name the pruner as their most important garden hand tool. With Pruners being such an important tool for gardeners, Richina offers a wide range of pruners so that you can choose the right tool for your specific pruning job: from Grass Shears Pruining Shears, Hedge Shers,Loppers and telescopic tree pruners.
How to choose the right Garden Pruner, Bypass or Anvil?
With a bypass cutting tool, you draw a curved or straight blade past another blade - this creates a scissor-like motion that works well for cutting live green plants. The spongy, firm outer wall surrounding the stem yields easily to that bypass motion.
With an anvil cutting tool, you bring down a straight blade against a wide anvil usually made of steel or hard rubber. Anvil pruners are better suited for dead and dried-out plants - the crushing motion causes the brittle stem to kind of explode and separate.
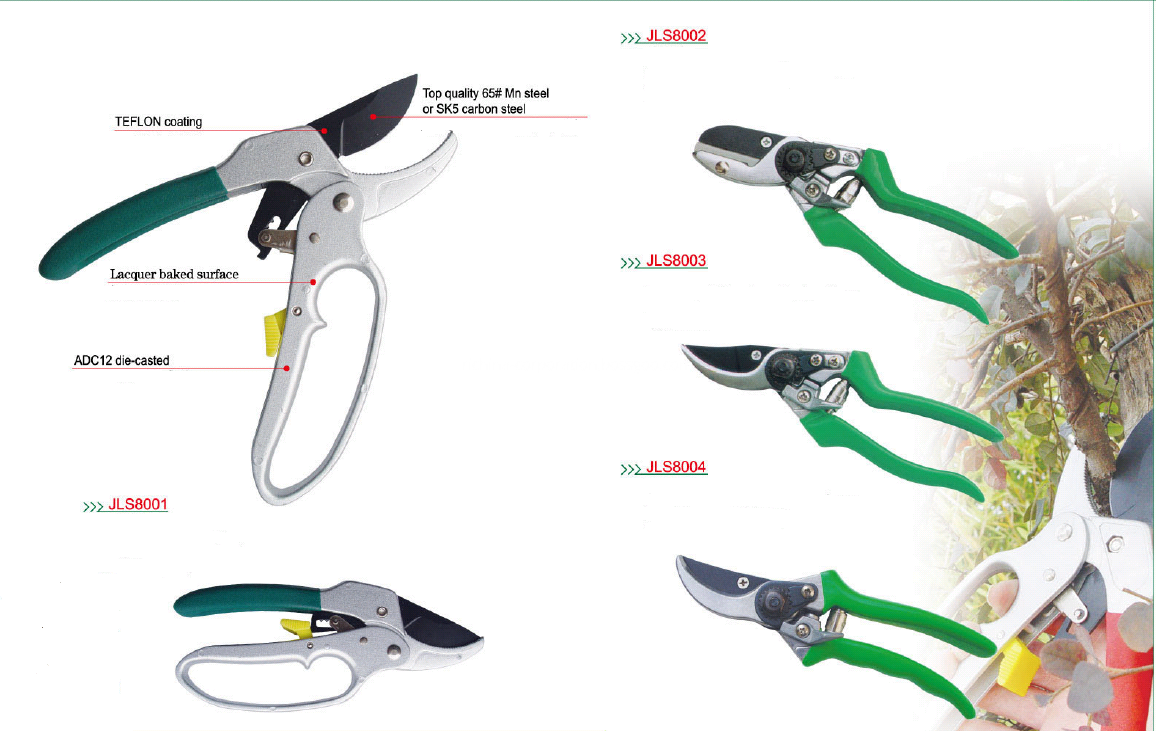
Garden Pruner
Garden Pruner,Garden Bypass Pruner,Hand Bypass Pruner,Garden Tree Pruner
Richina Ltd. , http://www.richina-corporation.com